Research Highlights
Members of the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) User Facility’s science team are major contributors to radiation and cloud research. Scientists and investigators using ARM publish about 150 peer-reviewed journal articles per year, and ARM data are used in many studies published by other scientific organizations. These documented research efforts represent tangible evidence of ARM’s contribution to advances in almost all areas of atmospheric radiation and cloud research.
Recent Highlights
Increasing model spatial resolution fails to reduce simulated storm biases
21 January 2025
Fast, Jerome D
Research area: Cloud-Aerosol-Precipitation Interactions
Supported by: ARM ASR
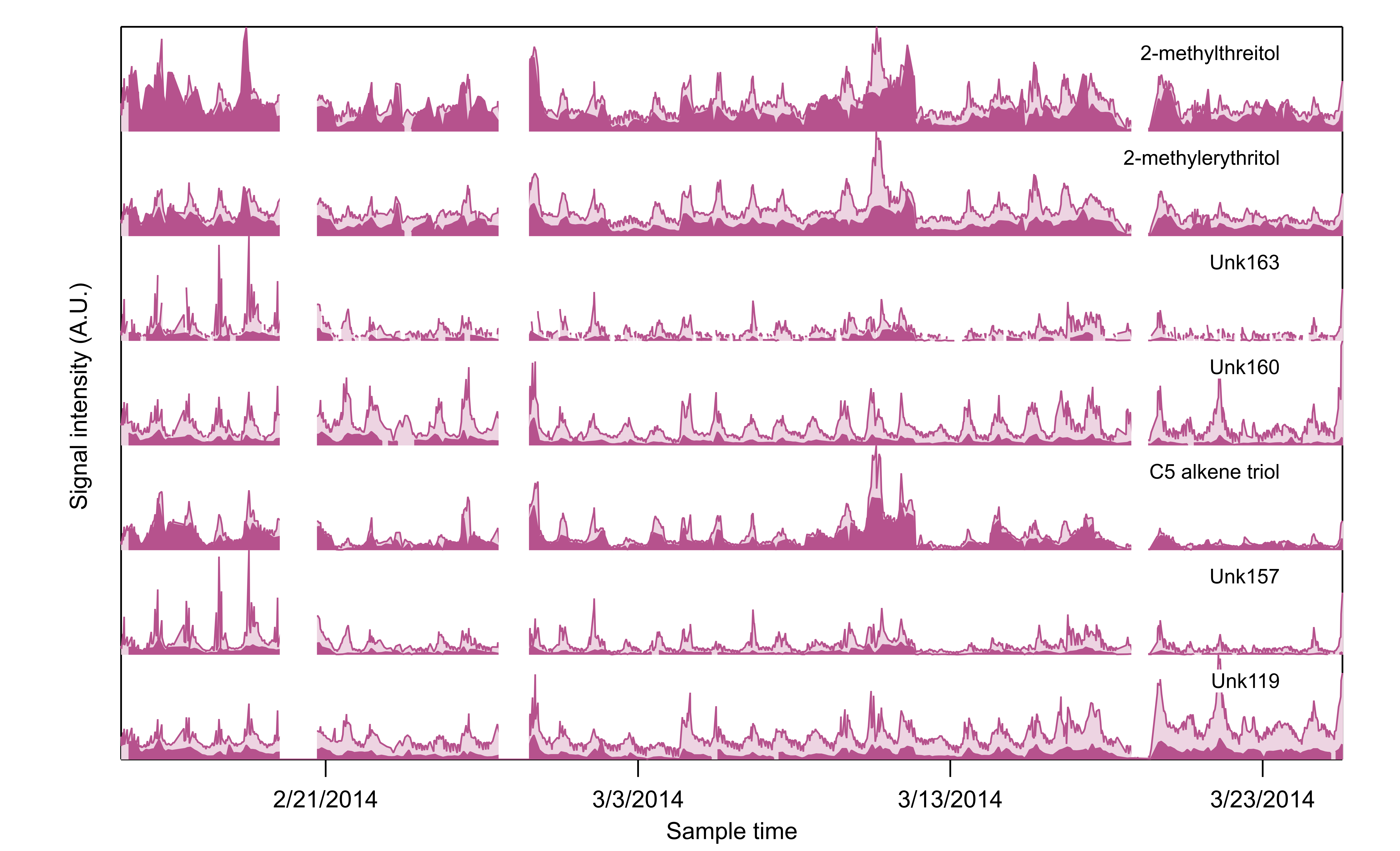
New methods for extracting more detail from existing data sets
21 January 2025
Isaacman-VanWertz, Gabriel
Research area: Aerosol Properties
Supported by: ASR
Bridging the data gap in Southern Hemisphere aerosol research
17 January 2025
Fast, Jerome D
Research area: Aerosol Processes
Supported by: ARM ASR
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.