New Data Product Determines Thermodynamic Phase of Cloud Hydrometeors
Published: 13 June 2023
Thermodynamic cloud phase identification is important to understand many cloud processes such as ice particle production, precipitation formation, and cloud life-cycle evolution, and it is essential to improve our understanding of cloud radiative properties and the atmospheric radiative budget.
Because ice particles and liquid droplets have distinct sizes, shapes, fall velocities, and refractive indexes, clouds with different thermodynamic structures have dramatically different radiative properties. Cloud phase identification is often required to retrieve cloud properties from remote-sensing measurements because most retrieval algorithms are developed for a specific cloud phase and type (Shupe et al. 2016).
To address this need, the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility created the Thermodynamic Cloud Phase value-added product (THERMOCLDPHASE VAP). Using a multisensor approach developed by Shupe (2007), this VAP combines measurements from active remote-sensing lidars, radars, microwave radiometers, and radiosondes to determine thermodynamic cloud phases at ARM sites.
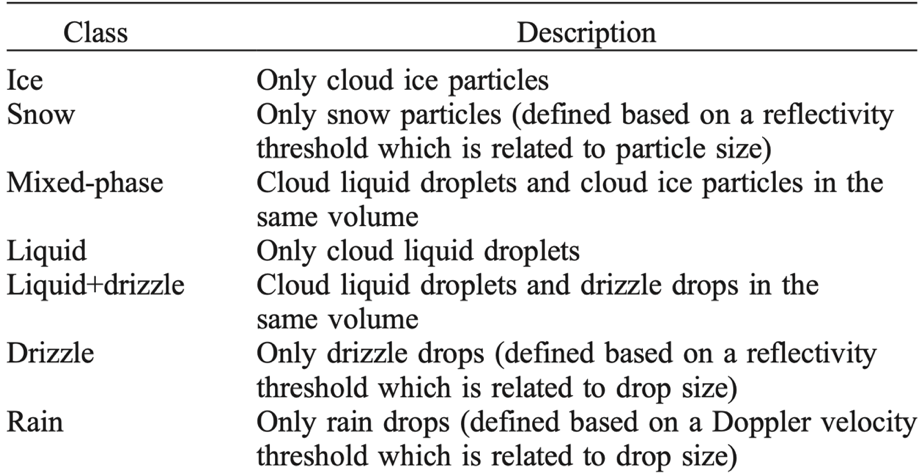

THERMOCLDPHASE evaluation data are now available for the North Slope of Alaska atmospheric observatory at Utqiaġvik from January 1, 2018, through December 31, 2022, and for Oliktok Point, Alaska, from July 1, 2015, through June 14, 2021.
Evaluation data are also available for the full duration of the following field campaigns except where noted:
- the 2015–2017 ARM West Antarctic Radiation Experiment (AWARE) at McMurdo Station, Antarctica
- the 2017–2018 Measurements of Aerosols, Radiation, and Clouds over the Southern Ocean (MARCUS) campaign between Hobart, Australia, and the coast of Antarctica
- the 2018–2019 Cloud, Aerosol, and Complex Terrain Interactions (CACTI) campaign near Córdoba, Argentina
- the 2019–2020 Cold-Air Outbreaks in the Marine Boundary Layer Experiment (COMBLE) near Andenes, Norway (COMBLE data are available from February 11 through May 31, 2020)
- the 2019–2020 Multidisciplinary Drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) expedition in the central Arctic.
Please note: Data previously released for the Utqiaġvik and COMBLE locations have been re-released to fix a problem in which the cloud phase layer classification labels were ordered incorrectly. Users who downloaded these data before April 2023 are encouraged to use the corrected data announced in this release.
Users are encouraged to provide feedback during this evaluation period to help improve the product. Future work will involve evaluating THERMOCLDPHASE data with aircraft measurements from ARM aerial campaigns and integrating user feedback into a production version of this VAP.
More information about THERMOCLDPHASE can be found on the VAP web page.
For questions or to give feedback about the evaluation data, please contact ARM translator Damao Zhang or VAP developer Maxwell Levin.
Access the THERMOCLDPHASE data in the ARM Data Center. (Go here to create an account to download the data.)
Data can be referenced as doi:10.5439/1871014.
References:
Shupe MD, JM Comstock, DD Turner, and GG Mace. 2016. Cloud property retrievals in the ARM Program. In The Atmospheric Radiation Program: The First 20 Years, pp. 1-20, https://doi.org/10.1175/AMSMONOGRAPHS-D-15-0030.1
Shupe MD. 2007. “A ground-based multisensor cloud phase classifier.” Geophysical Research Letters, 34(22), L22809, https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl031008
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















