Cloud Condensation Nuclei Vertical Profile Data Product Extended to ENA
Published: 15 January 2025
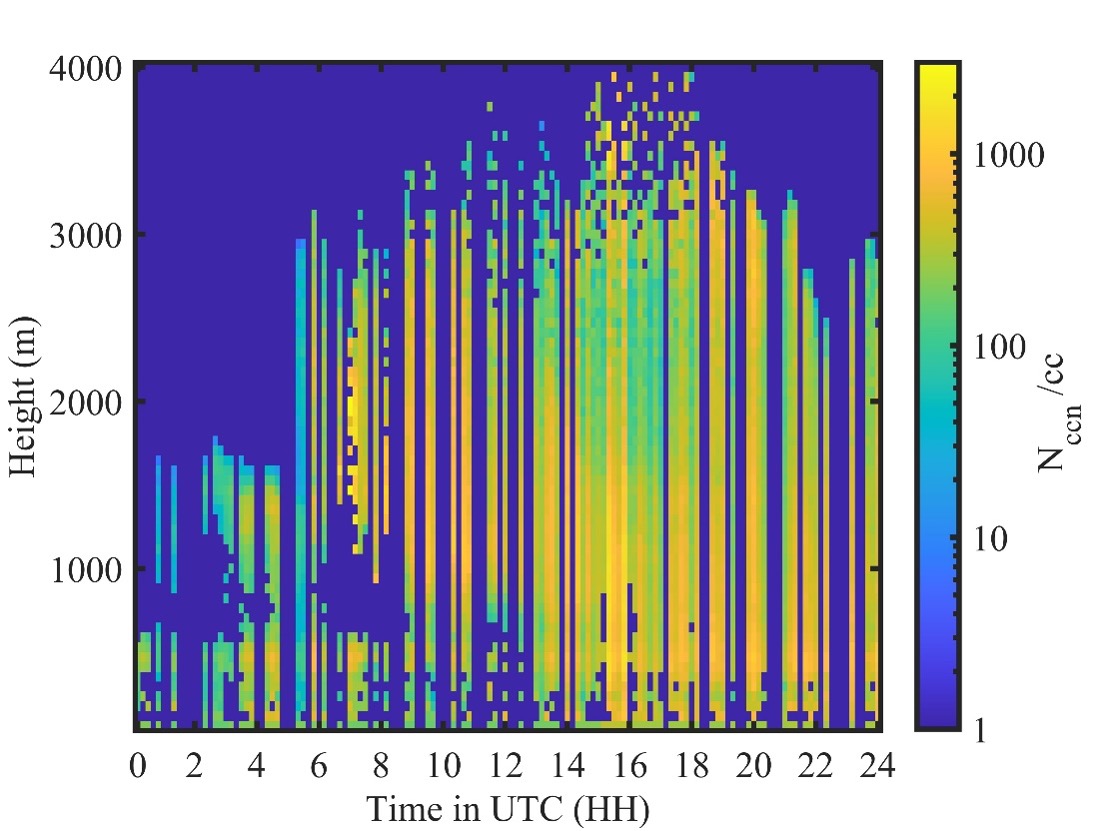
The Retrieved Number concentration of Cloud Condensation Nuclei value-added product (RNCCN VAP) is now available for evaluation for the Eastern North Atlantic (ENA) atmospheric observatory. This VAP provides the vertical distribution of cloud condensation nuclei (CCN) number concentrations at Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) User Facility sites for better representation of aerosol indirect effects in climate models.
RNCCN gives users the retrieved vertical profiles of CCN concentrations at the various supersaturation values measured by one- and two-column versions of the CCN particle counter. (Supersaturation occurs when the relative humidity is at least 100%.) RNCCN also routinely provides retrieved values of CCN near cloud base, which is a proxy for the aerosol that is entrained into clouds and leads to droplet formation.
The VAP uses a hygroscopicity parameter (gamma) based on the Hänel (1976) parameterization to calculate extinction changes due to hygroscopic growth of aerosol. Hygroscopicity is the ability of a particle to take up moisture from the environment and is important for understanding the variation in lidar-derived extinction with altitude.
For input, the VAP uses quality-controlled Raman lidar profiles (aerosol extinction and feature mask) and CCN spectral data in addition to the hygroscopicity data.
The ENA RNCCN evaluation data are available from January 20, 2017, to October 31, 2023. The data have 1-hour time resolution and 60-meter vertical resolution, and they are in netCDF format.
More information about the VAP, including its technical report, is available on the RNCCN web page.
Scientists can use RNCCN to help improve understanding of aerosol-cloud interaction treatment in global earth system models. Future work will involve extending this product to ARM’s Bankhead National Forest observatory in Alabama. The VAP team also plans to apply new quality control tests to further improve the data quality.
To provide feedback or ask questions about the evaluation data, please contact VAP science mentor Gourihar Kulkarni, VAP developer Chitra Sivaraman, or ARM aerosol translator John Shilling.
Access the RNCCN data in the ARM Data Center. (To download the data, first create an ARM account.)
To cite the data, please use doi:10.5439/1813858.
Reference: Hänel G. 1976. “The Properties of Atmospheric Aerosol Particles as Functions of the Relative Humidity at Thermodynamic Equilibrium with the Surrounding Moist Air.” Advances in Geophysics, 19:73-188, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2687(08)60142-9
Keep up with the Atmospheric Observer
Updates on ARM news, events, and opportunities delivered to your inbox
ARM User Profile
ARM welcomes users from all institutions and nations. A free ARM user account is needed to access ARM data.


















